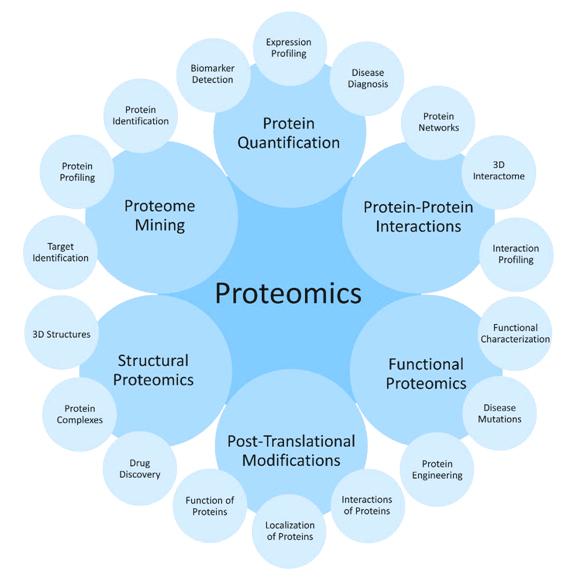
Evaluation fields of Proteomics. Credit: Adapted from Zengin T, Kiliç S, Yenigün U, et al. A smart way for talking with proteins; proteomics. MOJ Proteomics Bioinform. 2017;5(3):86-92. DOI: 10.15406/mojpb.2017.05.00160
Expert knowledge and support
The UK DRI Proteomics Platform provides researchers with access to advanced mass spectrometry instruments and bioinformatics expertise, facilitating comprehensive protein analysis across various neurodegenerative disease models.
The platform's expertise extends beyond sample processing to include study design, bioinformatics analysis, and sample preparation techniques. By offering these services internally, the UK DRI Proteomics Platform aims to streamline research efforts, reduce costs, and foster collaborations among UK DRI researchers.
This comprehensive approach to proteomics analysis is expected to accelerate the identification of early pathway perturbations and potentially reversible targets in neurodegenerative diseases, providing a strong foundation for future studies and therapeutic interventions.
Cutting edge tools and technology
The UK DRI Proteomics Platform employs a number of sophisticated techniques including:
Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) labeling: This method enables multiplex relative quantification of up to 18 samples simultaneously, allowing for deep proteome analysis of approximately 10,000 proteins from cell lysates. This approach significantly reduces time and cost for large-scale proteomic studies.
Data Independent Acquisition (DIA): This emerging technique offers comparable or sometimes superior performance to TMT, further enhancing the platform's capabilities for high-throughput protein quantification and identification.

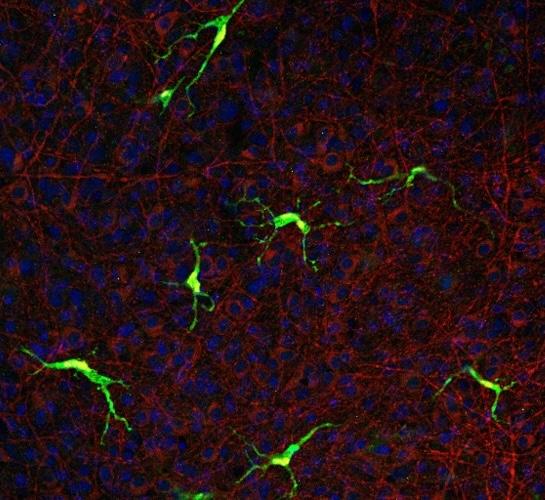
Microglia created using stem cells made from blood donated by people with Alzheimer's disease, as part of the UK DRI's IPMAR project: Credit: Hazel Hall-Roberts.
Collaborative projects across UK DRI
The UK DRI Proteomics Platform also collaborates closely with other major UK DRI platforms and projects including:
Integration with the IPSC Platform to Model Alzheimer's Disease Risk (IPMAR) in Cardiff, aiming to create a comprehensive proteomics database for induced pluripotent stem cell lines.
The Multi-'omics Brain Atlas Project (MAP) at Imperial to investigate relative protein level differences across various brain regions.
